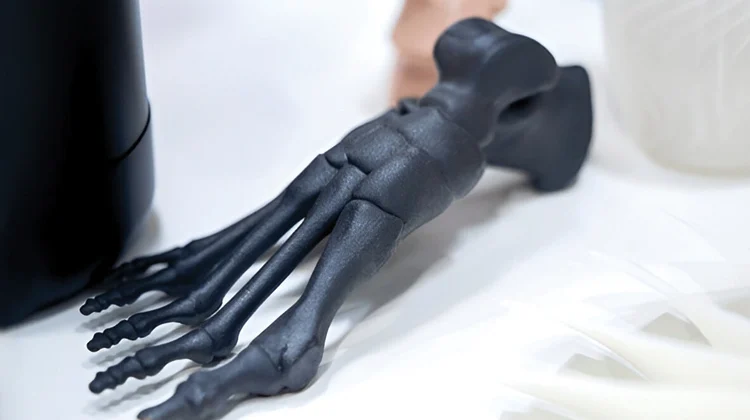
3D design, once a tool primarily used in industries like entertainment and manufacturing, has made significant strides in the medical field. This technology offers a wide range of applications, from improving patient care to advancing medical research. In this blog post, we will explore the various ways 3D design is being used in the medical industry and its potential to revolutionize healthcare.
Understanding 3D Design
3D design involves creating three-dimensional digital models of objects. These models can be manipulated, viewed from different angles, and even printed onto physical objects using 3D printing technology. In the medical context, 3D design enables the creation of highly accurate and detailed representations of human anatomy, medical devices, and surgical procedures.
Applications of 3D Design in Medicine
- Medical Imaging and Diagnosis
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D design allows medical professionals to visualize complex anatomical structures more comprehensively and intuitively. By converting 2D medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs into 3D models, doctors can gain a deeper understanding of a patient’s condition.
- Early Disease Detection: 3D models can help identify subtle abnormalities that may be difficult to spot on traditional 2D images. This early detection can lead to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
- Surgical Planning: Surgeons can use 3D models to plan complex procedures. By virtually simulating the surgery, they can identify potential challenges, optimize surgical techniques, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Patient-Specific Treatment
- Personalized Implants and Prosthetics: 3D design enables the creation of custom-made implants and prosthetics that perfectly match a patient’s unique anatomy. This ensures optimal fit, function, and comfort.
- Customized Surgical Instruments: Surgeons can design specialized surgical instruments tailored to a specific patient’s needs, improving precision and minimizing tissue damage.
- Drug Delivery Systems: 3D printing technology allows for the creation of personalized drug delivery systems, ensuring accurate dosing and targeted drug release.
- Medical Education and Training
- Interactive Learning Tools: 3D models provide a hands-on learning experience for medical students and professionals. They can explore anatomical structures in detail, understand complex medical concepts, and practice surgical techniques in a virtual environment.
- Patient Education: 3D models can be used to explain medical conditions and treatment plans to patients clearly and understandably, improving patient engagement and compliance.
- Research and Development
- Drug Discovery: 3D design helps researchers model the molecular structure of drugs and proteins, accelerating the drug discovery process.
- Tissue Engineering: 3D printing techniques are being used to create artificial tissues and organs, offering hope for regenerative medicine and transplantation.
The Future of 3D Design in Medicine
The potential of 3D design in the medical industry is vast and continues to evolve. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications, such as
- Virtual Reality Surgery: Surgeons may be able to perform complex procedures remotely using virtual reality technology. By immersing themselves in a 3D virtual environment, surgeons can gain a heightened sense of spatial awareness and precision.
- Artificial Intelligence-Powered Design: AI algorithms can analyze medical data and generate highly accurate 3D models, streamlining the design process. AI can identify patterns, make predictions, and optimize designs, leading to faster and more efficient development of medical devices and implants.
- Bio-printing of Organs: 3D printing may eventually enable the creation of fully functional organs for transplantation. By using biocompatible materials and living cells, scientists can “print” organs that are tailored to a patient’s specific needs, addressing the global organ shortage crisis.
Challenges and Considerations
While 3D design offers immense potential, some challenges need to be addressed:
- Cost: 3D design and printing technologies can be expensive, making them less accessible to healthcare providers in resource-limited settings.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory approval process for 3D-printed medical devices and implants can be complex and time-consuming.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of 3D design in medicine raises ethical questions, such as the potential for misuse and the impact on healthcare equity.
Conclusion
3D design has emerged as a powerful tool in the medical industry, transforming various aspects of healthcare. By enhancing visualization, enabling personalized treatment, improving education, and accelerating research, 3D design is poised to revolutionize the future of medicine. As technology continues to advance and challenges are addressed, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications of 3D design in the years to come.





