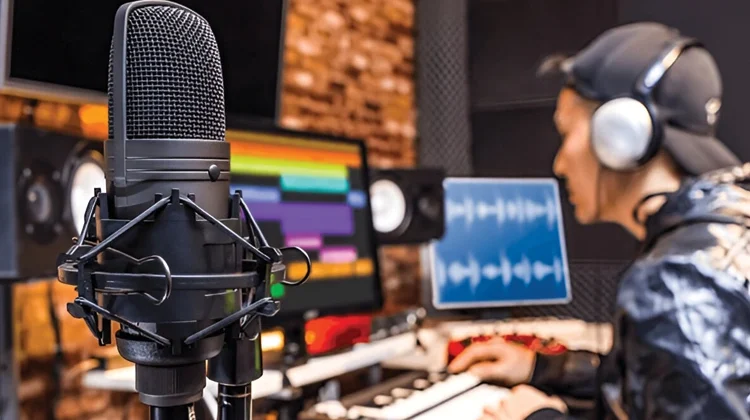
Audio editing is manipulating sound recordings to improve their quality, create desired effects, or combine multiple audio sources into a cohesive piece. It’s a crucial step in various fields, including music production, film-making, podcasting, and more.
The Art and Science of Audio Editing
Audio editing is both an art and a science. It requires a keen ear for detail, a solid understanding of audio principles, and the technical skills to manipulate sound. With the right tools and techniques, audio editors can transform raw audio into polished, professional-sounding recordings.
Key Audio Editing Techniques
- Noise Reduction: Eliminating unwanted background noise, such as hiss, hum, or clicks, to enhance audio clarity.
- Equalization: Adjusting the frequency balance of a recording to shape its tone and character.
- Compression: Controlling the dynamic range of a recording to reduce volume fluctuations.
- Reverb and Delay: Adding depth and dimension to audio by simulating the acoustic properties of different spaces.
- Fading and cross-fading: transitioning between audio clips to create seamless blends.
- Editing and Trimming: Cutting, pasting, and trimming audio clips to achieve the desired length and structure.
Prizing Audio Editing in Various Fields
Music Production:
- Mixing: Combining multiple tracks into a cohesive mix, balancing levels, and applying effects.
- Mastering: Preparing a final mix for distribution, optimizing loudness, and ensuring consistency across different playback systems.
Filmmaking:
- Dialogue Editing: Cleaning up dialogue, removing unwanted sounds, and adjusting levels for clarity.
- Sound Design: Creating sound effects and atmospheres to enhance the storytelling and emotional impact of a film.
- Music Scoring: Integrating music with the visuals to evoke specific emotions and enhance the overall mood.
Podcasting:
- Podcast Editing: Cleaning up audio, removing filler words, and adding intros and out-ros.
- Interview Editing: Structuring interviews, removing awkward pauses, and ensuring a smooth flow.
Audio Production:
- Radio Commercials: Creating engaging and attention-grabbing audio ads.
- Voiceovers: Editing voice recordings for clarity, consistency, and professional quality.
Audio Editing Tools and Software
There are many audio editing tools available, ranging from free options to professional-grade software. The popular choices include:
- Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs): Pro Tools, Ableton Live, Logic Pro, FL Studio
- Audio Editors: Audacity, Adobe Audition, iMovie, GarageBand
- Online Audio Editors: SoundCloud, Audacity Online, Online Audio Editor
Tips for Effective Audio Editing
- Listen: Pay close attention to the details of your audio and find areas that need improvement.
- Start with a Good Recording: A high-quality recording will make the editing process much easier.
- Use Headphones: Headphones give a more correct representation of the audio.
- Experiment with Different Techniques: Don’t be afraid to try new things and experiment with different effects.
- Take Breaks: Editing for long periods can strain your ears and eyes. Take regular breaks to rest.
- Back-Up Your Work: Always back up your audio files and project files to avoid data loss.
The Future of Audio Editing
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative audio editing tools and techniques. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already being used to automate certain tasks, such as noise reduction and equalization. Additionally, advancements in virtual and augmented reality may offer new possibilities for immersive audio experiences.
AI-Powered Audio Editing
- Automated Noise Reduction: AI algorithms can now accurately identify and remove noise from recordings, even in complex environments.
- Intelligent Equalization: AI-powered tools can analyze the characteristics of a recording and suggest optimal equalization settings.
- Real-Time Editing: AI can enable real-time editing and processing of audio, allowing for more interactive and dynamic experiences.
Immersive Audio Experiences
- Spatial Audio: Creating three-dimensional sound fields that surround the listener, providing a more immersive and realistic experience.
- Haptic Audio: Combining sound with physical sensations to enhance the emotional impact of audio content.
- Audio Augmented Reality: Integrating audio with visual elements to create interactive and immersive experiences.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future of audio editing looks promising, there are also challenges to overcome. One significant challenge is the ethical implications of AI-powered audio editing. For example, AI could be used to create deepfakes or manipulate audio recordings in harmful ways.
However, there are also opportunities to use AI for positive purposes, such as improving accessibility for people with hearing impairments or creating new forms of artistic expression.
Conclusion
Audio editing is a dynamic and ever-evolving field. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative tools and techniques that will transform the way we create, experience, and interact with sound. By staying informed about the latest developments and embracing new technologies, audio editors can continue to push the boundaries of their craft and create truly exceptional audio experiences.