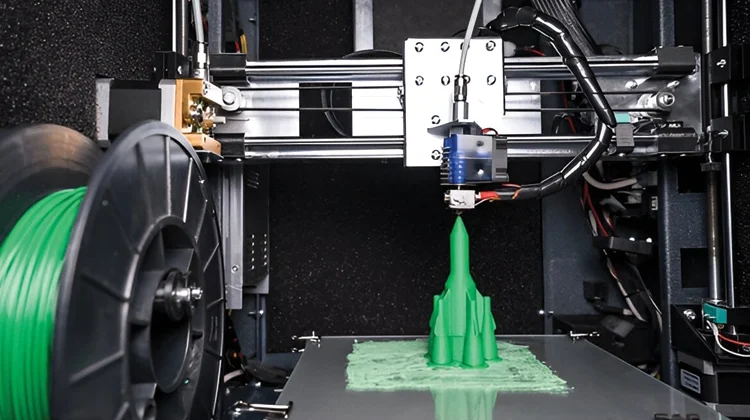
3D printing, a revolutionary technology, has emerged as a powerful tool for transforming digital designs into tangible objects. By laying materials, this process bridges the gap between the virtual and physical realms, offering unprecedented possibilities for innovation and creation.
Understanding 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing involves creating three-dimensional objects from digital models. This is achieved by adding layer upon layer of material, such as plastic, metal, or even biological substances, until the desired shape is formed. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility and customization, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs with remarkable precision.
The Role of 3D Models
3D models serve as the blueprint for 3D printing. These digital representations, created using specialized software, give a comprehensive definition of an object’s shape, dimensions, and material properties. With advancing computer-aided design (CAD) tools, designers and engineers can construct intricate 3D models, from simple prototypes to functional components.
The Impact of 3D Printing
The implications of 3D printing are far-reaching, extending across various industries and applications. In manufacturing, it offers the potential for rapid prototyping, reduced production costs, and customized product development. Healthcare benefits from 3D-printed medical implants, prosthetics, and surgical models. The architecture and construction sectors leverage this technology to create intricate building components and models. Even the art and design world has embraced 3D printing for producing unique and stunning pieces.
The Future of 3D Printing
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for 3D printing are expanding. Advancements in materials science are enabling the creation of stronger, more durable, and versatile objects. Integration with artificial intelligence and automation is streamlining the design and production processes. The growing accessibility of 3D printers is democratizing manufacturing and empowering individuals and small businesses to bring their ideas to life.
Case Studies: 3D Printing in Action
To illustrate the transformative power of 3D printing, let’s explore the real-world applications:
Healthcare Revolutionized
- Customized prosthetics: Patients with limb differences can now help with personalized prosthetics tailored to their specific needs. 3D printing allows for intricate designs that mimic the natural form and act of limbs, enhancing comfort and functionality.
- Surgical planning: Surgeons can create correct 3D models of patient anatomy, enabling precise pre-operative planning and simulation. This technology minimizes surgical risks and improves patient outcomes.
- Organ and tissue engineering: While still in its early stages, 3D printing holds immense promise for creating artificial organs and tissues for transplantation. This could revolutionize treating various diseases and conditions.
Manufacturing Reinvented
- Rapid prototyping: Engineers can produce physical prototypes of product designs, enabling rapid iteration and design optimization. This speeds up product development cycles and reduces time-to-market.
- Customized products: 3D printing allows for mass customization, enabling businesses to offer personalized products to meet individual customer preferences. This creates added revenue streams and strengthens customer loyalty.
- Supply chain optimization: By reducing the need for physical inventory, 3D printing can streamline supply chains and improve responsiveness to market demands.
Beyond Imagination
- Architecture and construction: 3D printing is being used to create complex architectural components, such as custom-designed facades and interior elements. This technology offers greater design freedom and construction efficiency.
- Aerospace and automotive industries: Lightweight and high-performance components are being produced using 3D printing, improving the performance and fuel efficiency of aircraft and vehicles.
- Art and design: Artists and designers are exploring the creative possibilities of 3D printing, producing intricate and visually stunning pieces that push the boundaries of traditional art forms.
Challenges and Opportunities
While 3D printing offers immense potential, it also presents challenges such as material limitations, build time, and cost. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these issues, paving the way for wider adoption and broader applications.
The future of 3D printing is undeniably bright. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, we can expect to see even more innovative and disruptive applications emerge across various industries. From personalized medicine to sustainable manufacturing, 3D printing has the power to transform the way we live and work.
Conclusion
3D printing represents a paradigm shift in the way we conceive, design, and manufacture products. By seamlessly converting digital 3D models into physical objects, this technology is revolutionizing industries and inspiring innovation. As technology matures, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking applications that will reshape our world.





